|
Reproductive aging is a natural process that impacts all people, yet it’s often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. As we age, our reproductive systems undergo significant changes that can impact fertility, hormonal balance, and overall health. Understanding these changes is crucial for making informed decisions about family planning and health management.
0 Comments
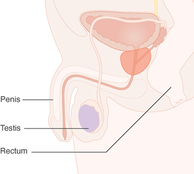
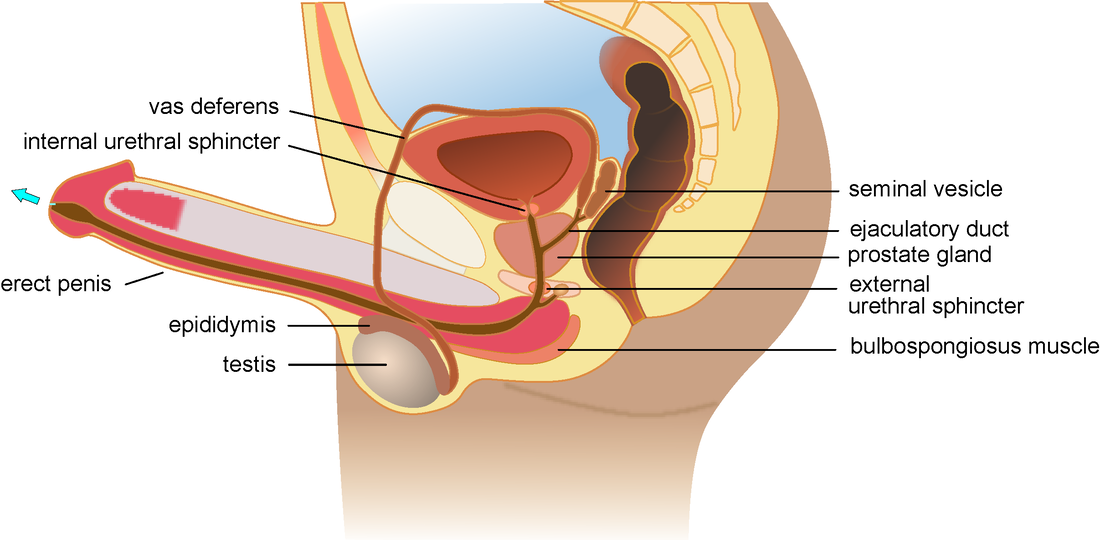
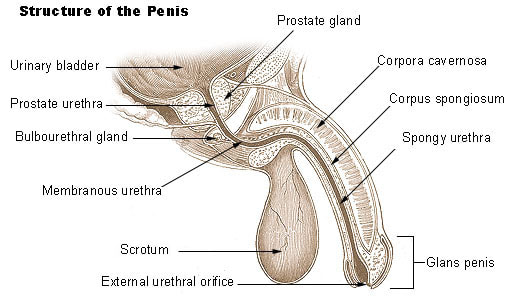
The prostate is part of the male reproductive system. A walnut-sized gland located between the male bladder and the penis, the prostate sits just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs from the bladder to the penis, through the center of the prostate.
(Image Source: Y. Rosen, MD) The production of sperm can be disrupted with a rise in temperature. Male thermal contraceptive methods (MTCs) involve heating the testicles inside the scrotum so that sperm production is slowed down. MTCs induce temporary infertility in men via a number of different methods, including applying hot water to the scrotum, generating heat on the testicles using ultrasound or heating pads, and creating artificial cryptorchidism (i.e., holding the testicles inside the abdomen) using specialized underwear.
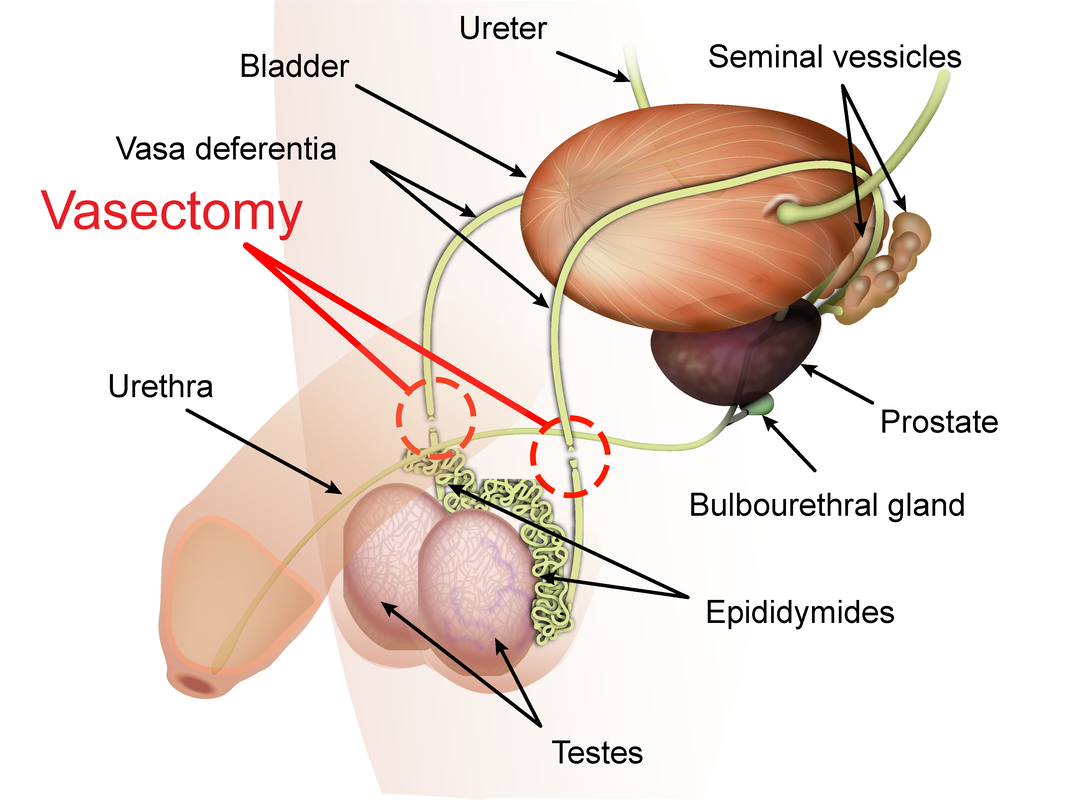
Vasectomy and condoms are the only current options for male contraception. The most popular form of long-acting male contraception is a vasectomy. Unfortunately, vasectomies are not considered truly reversible. Reversal of a vasectomy is often expensive, and requires a long surgery by a specialized provider.
The growth and development that people experience throughout their lifetime are accompanied by changes in their reproductive system. A person’s reproductive capacity differs between varying life stages. Ordinarily, sperm- and egg-producers become fertile and recognize themselves as reproductive beings during their adolescence or the years that follow puberty. As people continue to age and progress through their reproductive life cycle, natural age-related changes begin to affect everyone’s reproductive function.
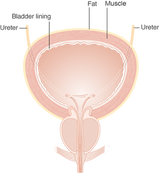
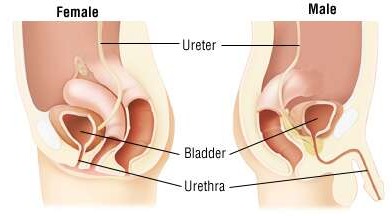
(Source: Cancer Research UK) The bladder, or urinary bladder, is a hollow muscular organ that stores urine from the kidneys before it is disposed of through urination. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical human bladder will hold between 10 and 16 fluid ounces before the urge to urinate occurs, but can hold considerably more. It is situated at the base of the pelvis in humans.
(Source: Cancer Research UK) The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals. The adult human rectum is about 4.7 inches (12 centimetres) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction, which is located at the end of the sigmoid colon.
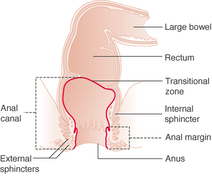
(Source: Cancer Research UK) The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract where stool (or feces) leaves the body. This is not to be confused with the rectum, which is the section of the digestive tract above the anus where stool is held before it passes out of the body. In humans, the anus is the external opening of the rectum, located inside the intergluteal cleft, known colloquially as the butt crack, and separated from the genitals by the perineum. Its primary purpose is to control the exit of feces from the body during defecation.
(Image courtesy of Wumingbai) Ejaculation is the discharge of semen from the male reproductive tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception.
Puberty is the process in which a human child’s body matures into an adult capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the ovaries in females and testes in males, also known as the gonads. In response to these signals, the gonads produce the hormones required for the physiological transformation of the human body, including changes to the sex organs and the stimulation of sexual desire in people (i.e., the libido).
(Image courtesy of K. D. Schroeder) Vasectomy is a surgical procedure for male contraception. It is intended to be a permanent form of contraception and, along with condoms, is one of the only methods of birth control available for men.
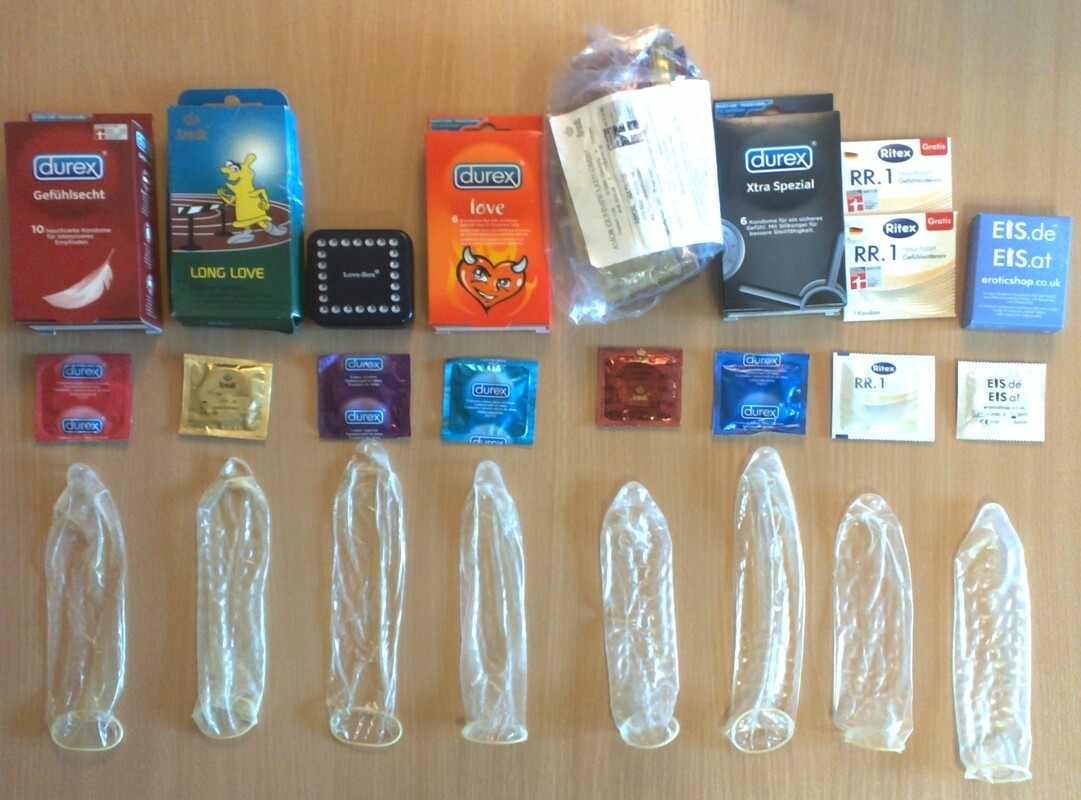
(Image courtesy of Corode) A condom is a barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI), and there are versions for both male and female users. A barrier device, or barrier method, is something that helps prevent pregnancy by blocking sperm from reaching and subsequently fertilizing the egg.
(Image courtesy of: DBCLS 統合TV, CC BY 4.0) Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell as they are responsible for cell respiration (the process which produces energy). Their most prominent function is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
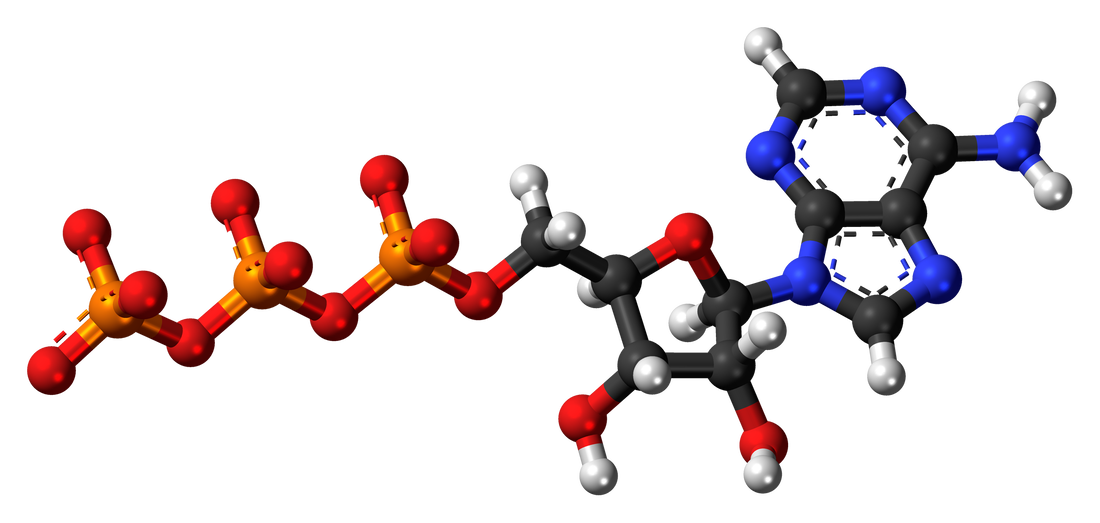
(Image courtesy of Jynto) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy storage molecule used to activate the reactions needed for growth and reproduction by all living organisms. It is an organic compound consisting of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups, and it is present in all living tissue.
(Image courtesy of Aethyta, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons) Testosterone is the primary sex hormone in males and is responsible for the development of male reproductive tissues (e.g., the testes and the prostate), as well as secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle mass and the growth of body hair. It is found in men and women, and is integral in regulating health and well-being, including maintaining bone mass.
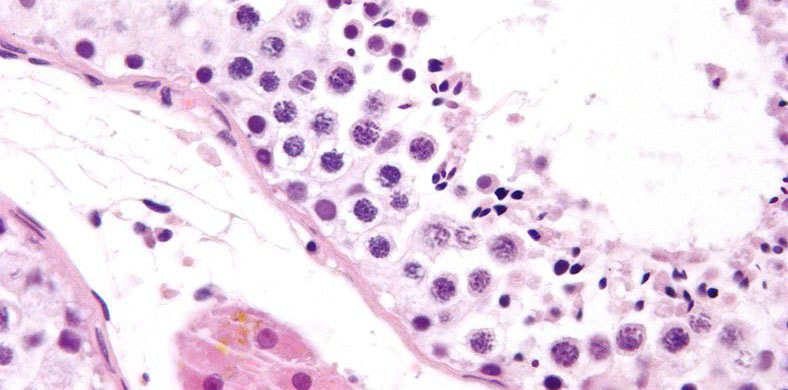
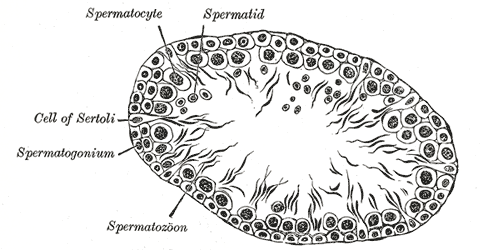
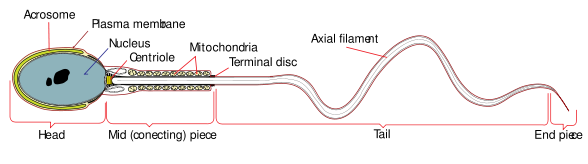
(Image courtesy of Nephron, CC BY-SA 3.0) Seminiferous Tubules are located in the testicles, the two oval-shaped organs on either side of a male’s penis. There are around 800 seminiferous tubules in each testicle, and this is where meiosis and subsequent development of spermatozoa occurs. In a mature adult male, each of these tubules creates thousands of sperm every second.
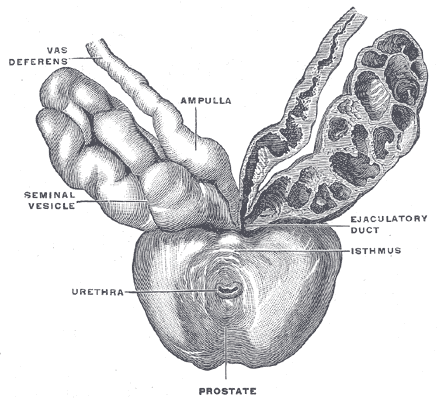
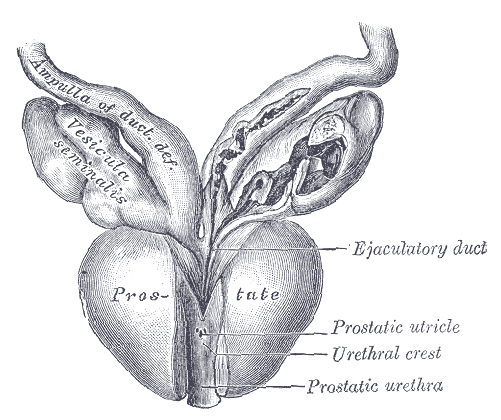
(Image courtesy of Henry Vandyke Carter, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons) The seminal vesicles or seminal glands are two tube-like glands located between the bladder and the rectum, behind the prostate. Each vesicle consists of a 3-5 cm coiled tube containing multiple pouches.
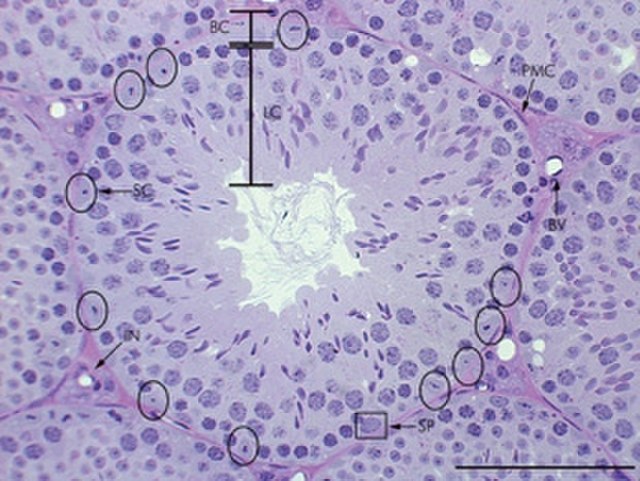
(Image courtesy of StemBook) The blood–testis barrier is a physical barrier between the blood vessels and the seminiferous tubules of the testes. The term is a bit misleading as it is not a blood-organ barrier, but rather one that is formed by the tight junctions between Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules. For this reason, this barrier is also referred to as the “Sertoli cell barrier”. The barrier isolates further developed germ cells from the blood.
(Image courtesy of by Henry Vandyke Carter) Named after Enrico Sertoli, an Italian physiologist, Sertoli cells are a specialized cell type found in the testicles. Specifically, they are located in the seminiferous tubules of the testes and they facilitate the production of new sperm, or, spermatogenesis.
(Source: Public Domain) Also known as Cowper's glands (named for English anatomist William Cowper), the bulbourethral glands are two small glands in the reproductive system of male humans, and many male mammals, that produce and secrete a pre-ejaculate fluid called Cowper's fluid, known colloquially as “pre-cum”.
(Image source: Henry Vandyke Carter, in public domain) The ejaculatory ducts are a part of the male anatomy that allows the flow of sperm from the testes through the reproductive system and eventually out through the urethra.
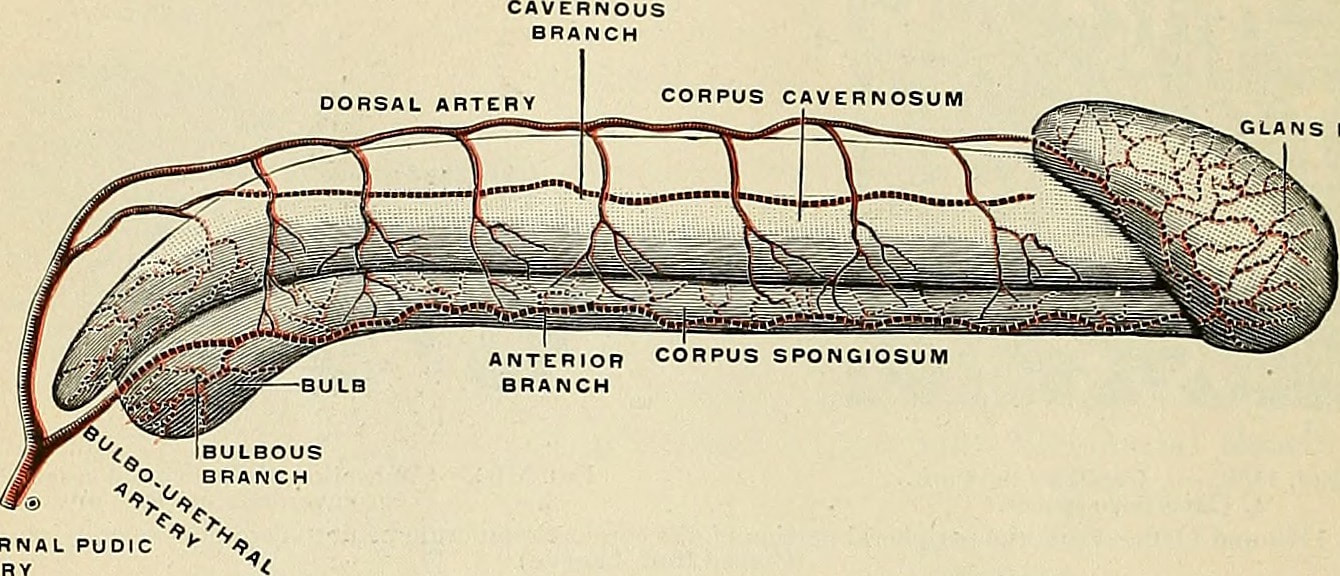
(Source: Internet Archive Book Images) The penis is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation, or sexual intercourse. It is the male genital organ of higher vertebrates that carries the duct for the transfer of sperm during sexual intercourse. In humans and most other mammals, it consists largely of erectile tissue and serves also for the elimination of urine. It lies between the legs of a man, above the testicles.
(Image source: Viva Differences) The urethra is a tube that connects the bladder to the urinary opening for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. It is the vessel through which urine passes after leaving the bladder, and the conduit in men for semen during sexual intercourse.
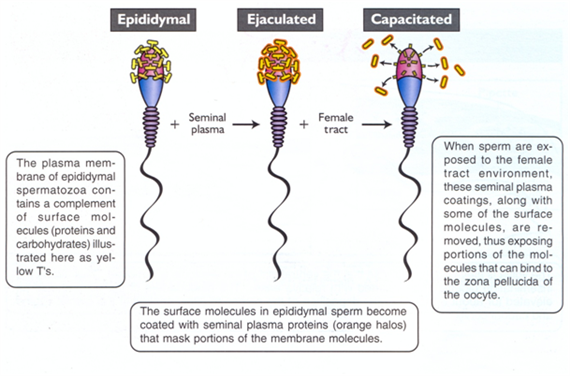
(Source: Ferenc Husvéth) Capacitation, generally speaking, is the change sperm undergo in the female reproductive tract that enables them to penetrate and fertilize an egg.
This step is a biochemical event; the sperm moves normally and looks mature prior to capacitation. It is important to note that once the sperm reaches the egg, it does not mean that it is capable of fertilizing it immediately. In order to fertilize the egg, the sperm must undergo the process of capacitation in the reproductive tract where a number of enzymes and signaling molecules are involved. This process can take around 10 hours, which means that the fertilization time is approximately 24 hours. (Image Source: Public Domain) We acknowledge that a person's sex and gender are two different things, as discussed here. Sex is defined as, "either of the two major forms of individuals that occur in many species and that are distinguished respectively as female or male, especially on the basis of their reproductive organs and structures."
In this article, we will be referring to "male" and "female" in reference to the scientific classification of a reproductive system and not a person's gender identity. |
Categories
All
Archives
June 2024
|
|
|
Donate to Male Contraceptive InitiativeYour generous donation makes a difference!
|
© Male Contraceptive Initiative. All rights reserved.








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
